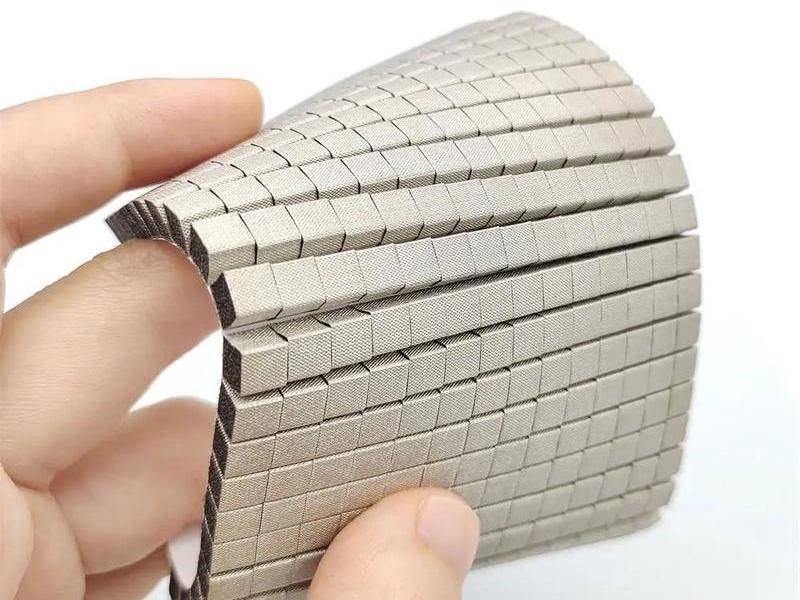
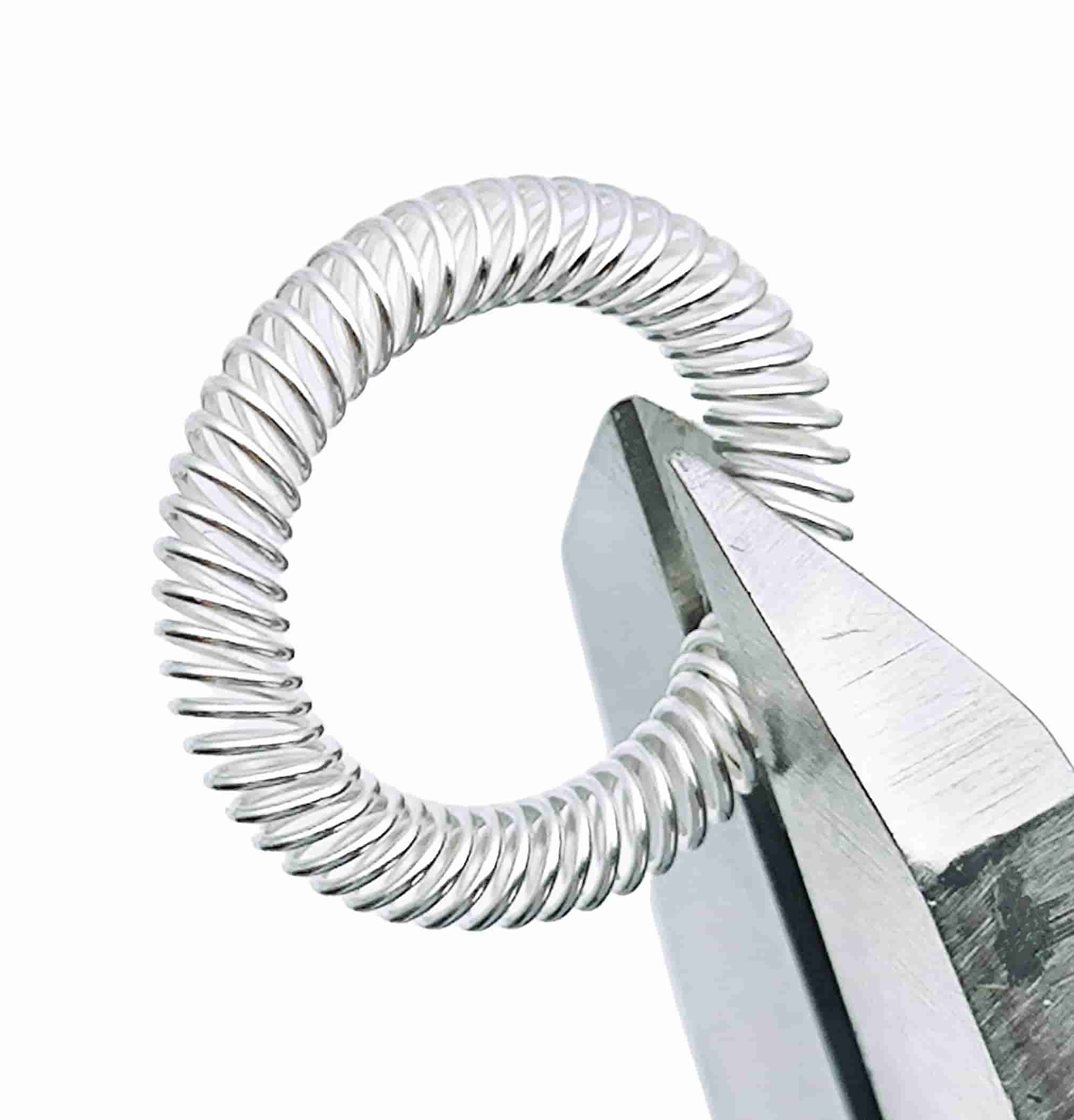
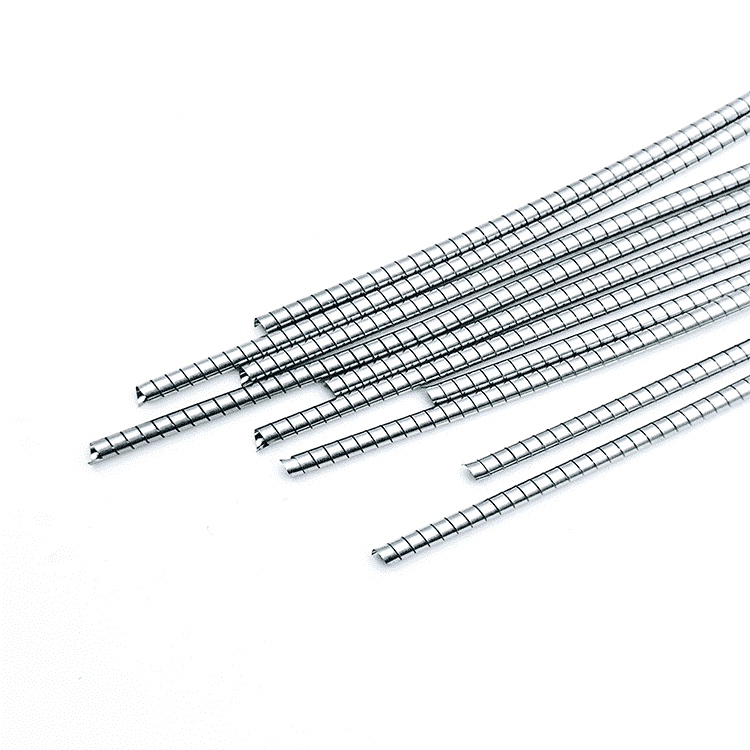
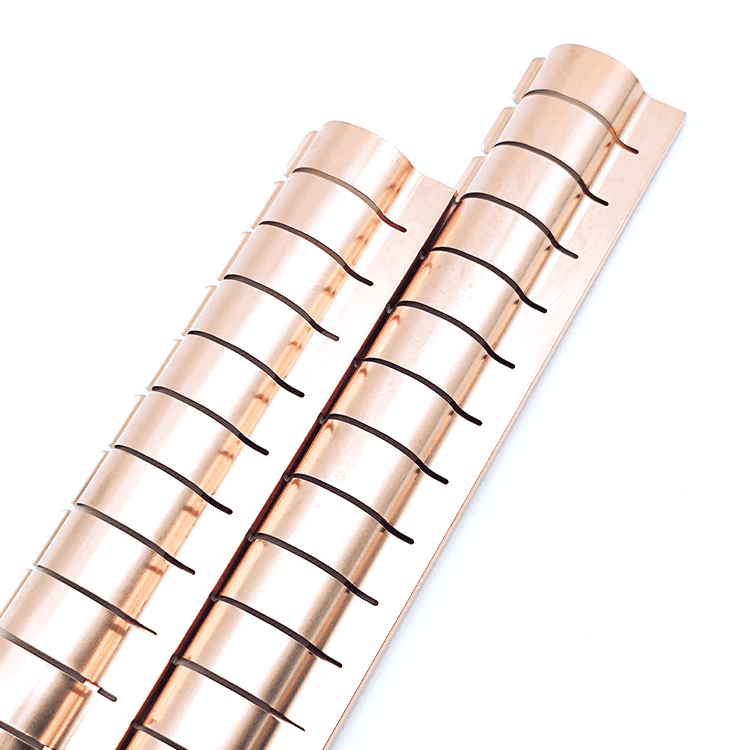
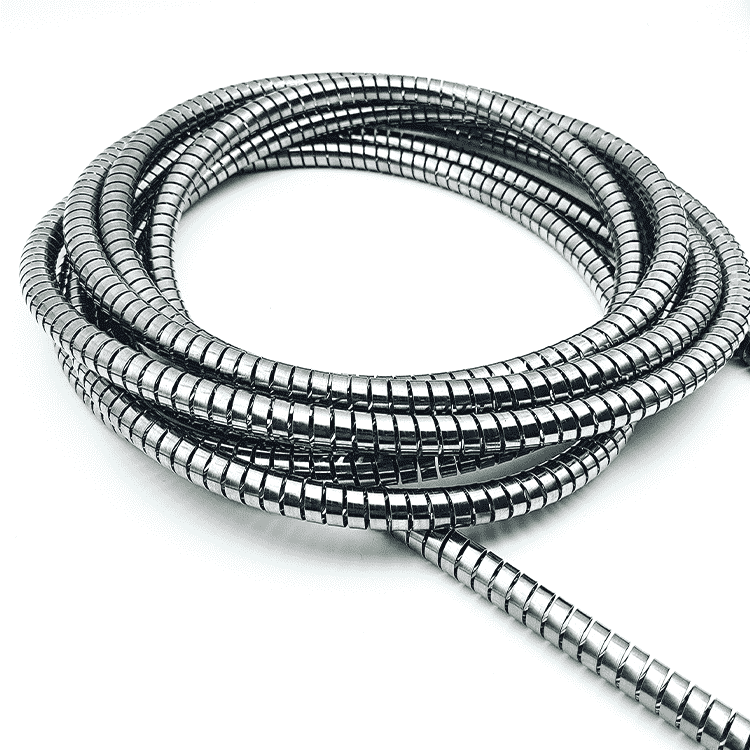
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks to protect sensitive electronic equipment
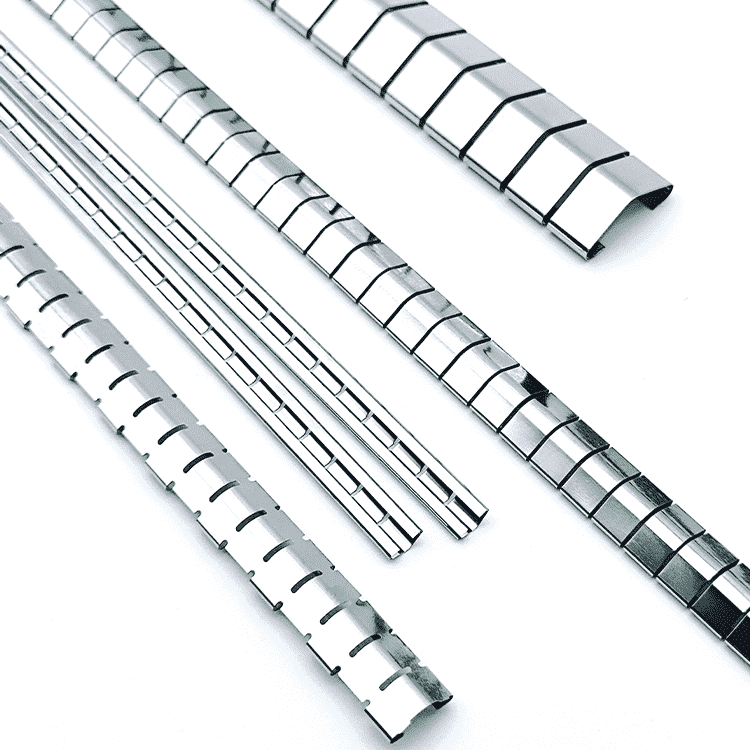

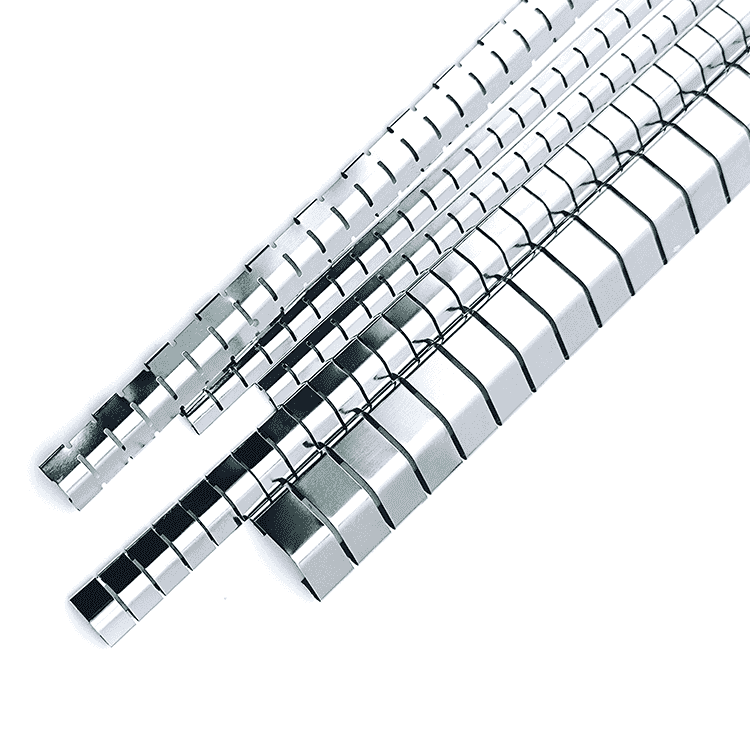
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks(Fingerstrips) are crucial components used in various industries to protect sensitive electronic equipment from electromagnetic interference (EMI). Made from specialized alloys such as beryllium copper, these materials ensure stable signal transmission while preventing external disturbances.
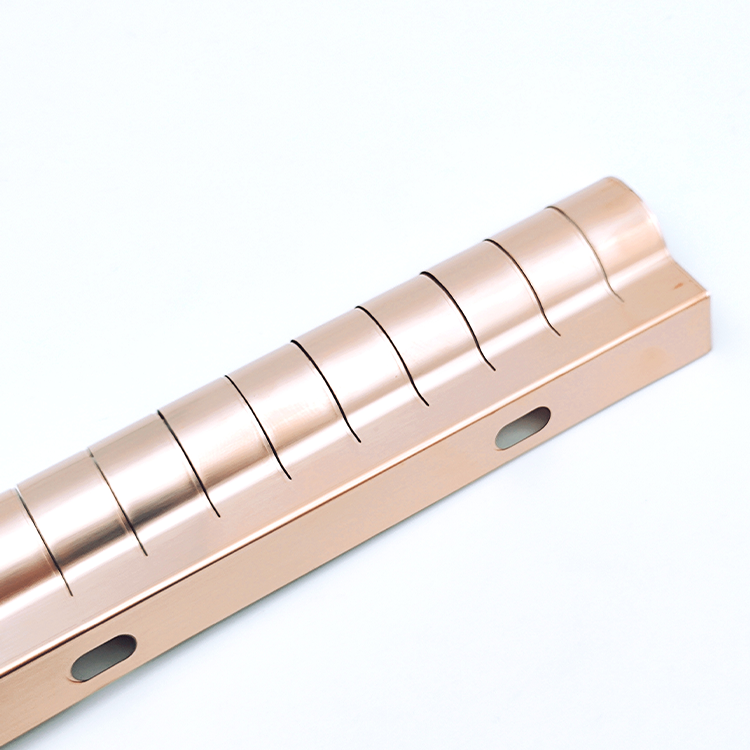

EMI Shielding Finger Stocks(Fingerstrips)
Table of Contents
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks(Fingerstrips) are crucial components used in various industries to protect sensitive electronic equipment from electromagnetic interference (EMI). Made from specialized alloys such as beryllium copper, these materials ensure stable signal transmission while preventing external disturbances. This article will delve into the intricacies of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks, exploring their design, types, performance standards, applications, installation methods, advantages, limitations, and future developments.
Introduction to EMI Shielding Finger Stocks
Electromagnetic interference can significantly impact the performance and reliability of electronic devices. EMI Shielding Finger Stocks are engineered to mitigate these effects, providing a barrier that reflects or absorbs electromagnetic waves. Their unique design allows them to create effective seals in various electronic applications, ensuring that sensitive components remain protected from external interference.
Basic Concepts
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks consist of resilient metal strips with a “finger-like” structure. This design enhances the ability of the material to conform to irregular surfaces and create a reliable contact. Beryllium copper is often the material of choice due to its excellent electrical conductivity, high tensile strength, and resistance to corrosion. These properties make it an ideal candidate for applications requiring both flexibility and durability.
Key Features and Types of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks
1. Types of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks are available in several configurations to meet various application needs:
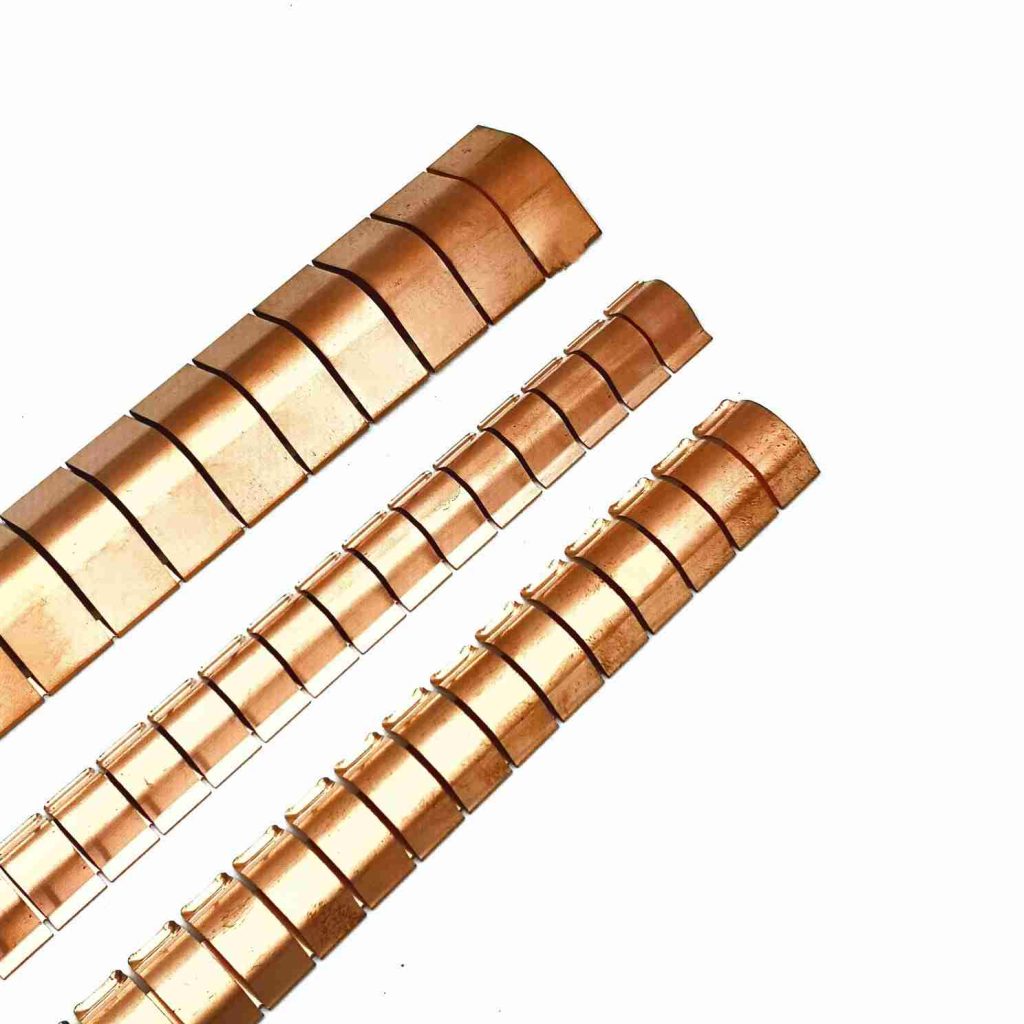
Stick-on mounting shielding fingerstrip(Adhesive-Mounted Finger Stocks)
- Design: These finger stocks feature a self-adhesive backing that allows for easy installation on surfaces with a gap of 6 to 11 mm.
- Applications: They are particularly effective in small bidirectional applications, such as mounting line cards in telecommunications equipment.
- Benefits: Their adhesive nature makes them easy to apply, providing high EMI shielding performance even in space-constrained environments.
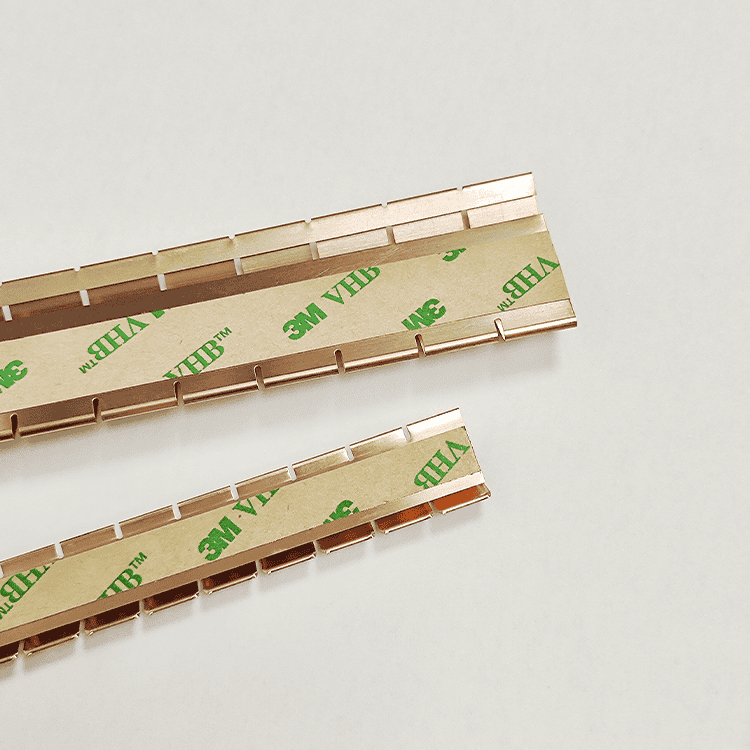

Clip-on mounting shielding fingerstrip(Clip-Mounted Finger Stocks)
- Design: This type is engineered for high-temperature environments or situations where adhesive mounting is not practical.
- Applications: Used in applications requiring robust shielding, they offer the same effectiveness as adhesive-mounted types.
- Performance: These stocks provide greater than 100 dB shielding effectiveness against 100 MHz plane waves and can be easily installed by pressing or sliding into place.
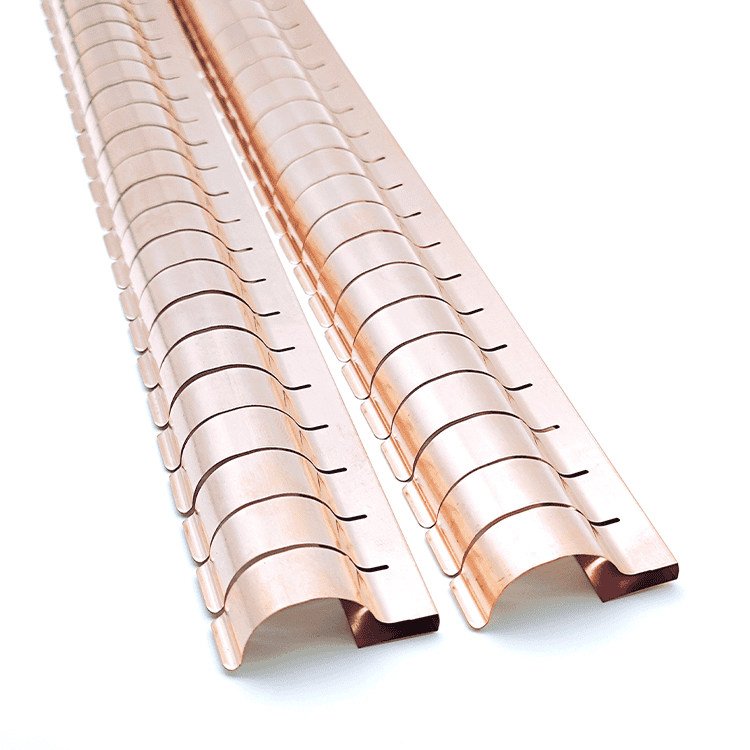
Circular fingerstrip(Round Finger Stocks)
- Design: Circular finger stocks are used for grounding and EMI shielding in high-frequency devices, forming large diameter circular contact rings.
- Applications: Ideal for grounding and EMI shielding situations requiring dynamic ranges and circular contacts.
- Features: They possess excellent elasticity and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for a variety of environments.

2. Design Characteristics
The design of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks plays a critical role in their effectiveness:
- Finger Structure: The “finger” design allows the material to conform to surfaces, enhancing contact and providing effective shielding.
- Material Properties: The use of alloys such as beryllium copper ensures high conductivity and resistance to environmental factors like corrosion and temperature fluctuations.
- Durability: EMI Shielding Finger Stocks are built to withstand physical stress, maintaining performance over long periods.
Performance Standards
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks must meet specific performance standards to ensure their effectiveness in shielding applications. These standards can vary by region and application, but generally, they fall into national and military categories.
National Standards
Class C Standards
- Magnetic Field:
- 10 KHz ≥ 70 dB
- 150 KHz ≥ 95 dB
- Electric Field:
- 200 KHz-50 MHz ≥ 100 dB
- Plane Wave:
- 50 MHz-1 GHz ≥ 100 dB
- Microwave:
- 1 GHz-10 GHz ≥ 100 dB
Class B Standards
- Magnetic Field:
- 10 KHz ≥ 40 dB
- 100 KHz ≥ 70 dB
- Plane Wave:
- 30 MHz-1 GHz ≥ 80 dB
- Microwave:
- 1 GHz-6 GHz ≥ 80 dB
Military Standards
Military standards for EMI shielding often exceed national standards, ensuring robust protection in demanding environments.
Class B Military Standards
- Magnetic Field:
- 10 KHz-100 KHz 15-37 dB
- 100 KHz-3 MHz 37-70 dB
- 3 MHz-20 MHz 70 dB
- Electric Field:
- 20 MHz -1 GHz 70 dB
- Microwave:
- 1 GHz-18 GHz 60-70 dB
Class C Military Standards
- Magnetic Field:
- 10 KHz-100 KHz 60-80 dB
- 100 KHz-1 MHz 80-100 dB
- 1 MHz-20 MHz 100 dB
- Electric Field:
- 20 MHz -1 GHz 100 dB
- Microwave:
- 1 GHz-18 GHz 100 dB
Class D Military Standards
- Magnetic Field:
- 10 KHz-100 KHz 87-108 dB
- 100 K-300 KHz 108-120 dB
- 300K-20MHz 120 dB
- Electric Field:
- 20 MHz -1 GHz 100 dB
- Microwave:
- 1 GHz-10 GHz 120 dB
- 10 GHz-18 GHz 110 dB
- 18 GHz-40 GHz 90 dB

Applications of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks find use in a wide array of applications across various industries. Their ability to provide reliable shielding makes them indispensable in the following areas:
Telecommunications Equipment
In telecommunications, EMI shielding is critical for ensuring stable signal transmission. Finger stocks are used to mount line cards and other sensitive components, protecting them from EMI that could disrupt service. Their easy installation and effective performance make them a preferred choice in this sector.
High-Frequency Devices
High-frequency applications, such as radar systems and communication devices, require effective grounding and shielding. EMI Shielding Finger Stocks are designed to handle these high-frequency signals while maintaining signal integrity, making them essential for manufacturers in this field.
Military Equipment
The military industry demands the highest standards of performance and reliability. EMI Shielding Finger Stocks that meet military specifications are crucial for protecting sensitive equipment from EMI in various operational environments. Ongoing developments aim to enhance these materials to meet even more stringent requirements.
Other Electronic Devices
Various electronic devices, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery, encounter EMI/RFI and ESD challenges. EMI Shielding Finger Stocks help mitigate these issues, ensuring the proper functioning of devices and reducing the risk of electrical noise and corrosion between different metals.
Installation Methods
Proper installation of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks is essential for optimal performance. There are several installation methods depending on the type of finger stock being used:
Adhesive Installation
Using pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) is a common method for mounting finger stocks. This approach is straightforward and allows for precise placement on the required surfaces.
Clip Installation
Clip-mounted finger stocks are installed by pressing or sliding them into position. This method is particularly beneficial in high-temperature environments where adhesives may fail.
Threaded Installation
For applications needing environmental sealing alongside EMI shielding, threaded installations may be employed. This method provides a robust solution, ensuring the stocks remain securely in place under various conditions.

Advantages of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks offer numerous benefits, making them a preferred choice for many applications:
High Shielding Effectiveness
These materials provide stable shielding across a wide range of frequencies, ensuring reliable protection against EMI in diverse environments.
Temperature Resistance
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks can perform well under extreme temperature conditions, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Fatigue Resistance
With the capability to withstand repeated compressions without deformation, these finger stocks offer long-term reliability, which is crucial for applications subject to regular mechanical stress.
Flexibility
The design of finger stocks allows them to adapt to different sizes and shapes of interfaces, providing versatile installation options.
Limitations of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks
Despite their advantages, EMI Shielding Finger Stocks do have limitations:
Higher Costs
Quality EMI shielding materials, particularly those meeting military standards, can be more expensive than standard materials. This cost factor can be a consideration for manufacturers and users.
Lack of Environmental Sealing
Most EMI Shielding Finger Stocks do not provide environmental sealing unless specifically designed to do so. This limitation may necessitate additional sealing solutions in certain applications.

Future Developments
The future of EMI Shielding Finger Stocks looks promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at enhancing their performance and applicability. Key areas of focus include:
Material Innovations
Research is being conducted on new materials and alloys that could offer better shielding effectiveness, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors.
Improved Manufacturing Techniques
Advancements in manufacturing processes could lead to more precise and efficient production methods, potentially reducing costs and improving the quality of the final products.
Expanded Applications
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for effective EMI shielding solutions is likely to increase. EMI Shielding Finger Stocks may find new applications in emerging technologies, such as electric vehicles, wearable electronics, and advanced telecommunications systems.
Conclusion
EMI Shielding Finger Stocks are an essential component in the fight against electromagnetic interference. Their unique design and material properties enable effective shielding across various applications, ensuring the reliability and performance of sensitive electronic equipment. As technology advances, the need for effective EMI shielding will only grow, making these finger stocks a critical aspect of future electronic designs. Understanding their features, installation methods, and applications will help manufacturers and engineers make informed choices when selecting shielding solutions for their projects.
You May Also Like
-
 EMI Shielding Spiral Tube Gaskets
EMI Shielding Spiral Tube GasketsEMI/EMC Shielding | RFI Shielding | EMI Gaskets
RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gasket
EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) shielding spiral tube gaskets are critical components in many electronic and industrial applications, designed to protect sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference while also maintaining structural integrity in challenging environments. One of the primary concerns with these gaskets is their susceptibility to corrosion, which can compromise their effectiveness and longevity. This article explores strategies to enhance the corrosion resistance of EMI shielding spiral tube gaskets, focusing on material selection, surface treatments, design optimization, and maintenance practices. Understanding EMI Shielding Spiral Tube GasketsFunctionality and ImportanceComposite MaterialsAdvantages of Composite MaterialsMaintenance and CareInspectionImportance of Regular InspectionCleaningBenefits of Regular CleaningConclusion EMI Shielding Spiral Tube Gaskets Understanding EMI Shielding Spiral Tube Gaskets EMI shielding spiral tube gaskets are engineered to create a reliable seal between two surfaces, preventing electromagnetic waves from penetrating and interfering with the operation of electronic devices. They are typically made from conductive materials that offer both mechanical flexibility and electrical conductivity. However, the presence of moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures can lead to corrosion, undermining their effectiveness. Thus, enhancing corrosion resistance is essential for ensuring their longevity and performance. Functionality and Importance EMI shielding spiral tube gaskets serve multiple functions, including: Electromagnetic Shielding: They block unwanted electromagnetic radiation, preventing......
-
 Electrically conductive foam for a wide range of applications
Electrically conductive foam for a wide range of applicationsShielding Gasket Solutions and Materials
Electrically conductive foam
Electrically conductive foam is an innovative material designed to combine the softness, flexibility, and compressibility of traditional foam with the ability to conduct electricity. This unique combination of properties makes conductive foam ideal for a variety of industries where both cushioning and electrical functionality are required, such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and military hardware. What is Electrically Conductive Foam?Key Characteristics of Electrically Conductive FoamApplications of Electrically Conductive FoamManufacturing Process of Electrically Conductive FoamAdvancements and Trends in Electrically Conductive FoamConclusion What is Electrically Conductive Foam? Electrically conductive foam is a specialized foam material that has been infused or coated with conductive materials such as carbon, silver, nickel, or copper. These conductive particles provide the foam with its unique ability to transmit electricity, allowing it to function as both a cushioning material and an electrically active component. The foam itself is typically made from polyurethane, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), or other flexible polymers, which provide the base mechanical properties such as compressibility, resilience, and environmental resistance. The conductive fillers are either mixed into the foam during production or applied as a surface coating, depending on the application’s requirements. Key Characteristics of Electrically Conductive Foam Electrically conductive foam offers several distinctive properties......
-
 Conductive Contact Finger Springs / Canted Coil Springs for Conducting Electricity:Versatile Solutions for Reliable Electrical Connections
Conductive Contact Finger Springs / Canted Coil Springs for Conducting Electricity:Versatile Solutions for Reliable Electrical ConnectionsHanda Canted Coil Springs
Electrical conducting springs
conductive contact finger springs /conducting canted coil springs The Challenge of Maintaining Reliable ConductivityConductive Contact Finger Springs: A Reliable SolutionConsistent Force Across Wide Deflection RangeMultiple Contact Points for Reliable ConductivitySuperior Conductive PropertiesEfficient Heat ManagementEMI/RF Shielding CapabilitiesSupporting SWaP (Space, Weight, and Power) RequirementsLow Insertion Force for Delicate ApplicationsDurability in Challenging ConditionsCleanliness and Sterilization in Medical ApplicationsConclusion: The Versatility of Electrically Conductive Contact Finger Springs Electrically conductive contact finger springs are specialized components designed to serve as highly efficient electrical conductors in applications requiring robust electrical connections, even under challenging conditions such as vibration, dynamic loads, and mechanical shock. These finger springs are often used in various industrial, automotive, and high-tech environments where maintaining electrical integrity is crucial. This article will explore the advantages, applications, and technical considerations of electrically conductive contact finger springs, with an emphasis on their use in environments where consistent electrical conductivity is critical. The Challenge of Maintaining Reliable Conductivity In many industrial settings, maintaining a reliable electrical connection can be a significant challenge. Various operational conditions, such as vibration, mechanical shock, and dynamic loads, can make it difficult for traditional electrical connections to remain secure. For instance, in the petrochemical industry, downhole tools are exposed to extreme......
-
 Handa Beryllium-Copper Fingerstrips/Fingerstocks with a variety of benefits
Handa Beryllium-Copper Fingerstrips/Fingerstocks with a variety of benefitsFingerstrips
Beryllium-copper fingerstrips series
https://www.handashielding.com/contact-us.html Handa Beryllium-Copper Fingerstrips/Fingerstocks with a variety of benefits Introduction to Handa Beryllium-Copper Fingerstrips/FingerstocksOverview of Beryllium-Copper as a MaterialKey Features of Handa Beryllium-Copper Fingerstrips/FingerstocksApplications of Handa Beryllium-Copper Fingerstrips/FingerstocksAdvantages of Using Handa Beryllium-Copper Fingerstrips/FingerstocksInstallation and Best PracticesConclusion Introduction to Handa Beryllium-Copper Fingerstrips/Fingerstocks Handa beryllium-copper fingerstrips, also known as fingerstocks, are highly efficient EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) shielding components. These products are essential in various industries, where sensitive electronic equipment requires protection from external electromagnetic and radio frequency interference (RFI). Beryllium-copper is a popular material for this purpose due to its outstanding combination of mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and durability. As electronic devices become smaller and more integrated, the demand for highly effective shielding materials has increased. Handa beryllium-copper fingerstrips/fingerstocks provide a versatile solution for shielding gaps, seams, and other openings where electromagnetic radiation can escape or penetrate. This article will explore the design, features, applications, and benefits of these specialized shielding components. Overview of Beryllium-Copper as a Material Before diving into the specifics of Handa's fingerstrips, it is crucial to understand the material used—beryllium copper. Beryllium copper is a copper alloy with small amounts of beryllium (typically 0.5% to 3%). This combination offers several advantages: High Conductivity: Copper is known for its......
-
 EMI Shielding Helical Springs with Unique Function
EMI Shielding Helical Springs with Unique FunctionEMI/EMC Shielding | RFI Shielding | EMI Gaskets
Handa Shielding offers various types of shielding products. These products come in different shapes and materials, and they each have their own unique function. In this article, we will take a look at the EMI shielding aspect and explore the function and advantages of EMI Shielding Helical Springs, which are designed to protect electronic devices from electromagnetic interference. Understanding Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)What Are EMI Shielding Helical Springs?Key Characteristics of EMI Shielding Helical SpringsStructure and Function of EMI Shielding Helical SpringsMaterials Used in EMI Shielding Helical SpringsApplications of EMI Shielding Helical SpringsInstallation and Usage of EMI Shielding Helical SpringsBest Practices for EMI Shielding Helical SpringsConclusion EMI Shielding Helical Springs with Unique Function Understanding Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Electromagnetic interference (EMI) refers to unwanted noise or interference in an electrical pathway or circuit caused by external sources. Also known as radio frequency interference, EMI can significantly impact the performance and functionality of electronic devices. Key aspects of EMI: It can cause electronics to operate inefficiently, malfunction, or cease functioning entirely EMI can arise from both natural and man-made sources Proper mitigation strategies are essential to minimize its effects What Are EMI Shielding Helical Springs? EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) Shielding Helical Springs are specialized mechanical......