How RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets work to block electromagnetic interference?
RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets are specialized components designed to protect electronic devices from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). Understanding how these gaskets work involves grasping the principles of EMI shielding and the unique construction of spiral gaskets.
Table of Contents
Understanding Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI)
Before delving into the specifics of RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets, it’s crucial to understand the underlying issues these components are designed to mitigate: Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI). These terms are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct definitions that are important in the context of shielding technology.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
EMI refers to the disruption that occurs when an external electromagnetic field affects the operation of an electronic circuit. This can lead to a range of issues, from minor performance degradation to complete operational failure. EMI is a broad term that encompasses all frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that can interfere with the normal functioning of electrical and electronic devices.
EMI can originate from various sources, both natural and man-made. Natural sources include solar flares, lightning, and even cosmic radiation. Man-made sources are more common and include anything from power lines and electrical motors to wireless communication devices and microwave ovens. The consequences of EMI are particularly severe in environments with high concentrations of sensitive electronics, such as hospitals, military installations, and industrial settings.
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI)
RFI is a subset of EMI, specifically referring to interference that occurs within the radio frequency spectrum, typically from 3 kHz to 300 GHz. RFI primarily affects wireless communication systems, including radio, television, cellular phones, and Wi-Fi networks. When RFI occurs, it can result in the loss of signal, degradation of data transmission quality, and, in severe cases, total communication failure.
RFI can be caused by both intentional and unintentional sources. Intentional sources include devices like jammers or radar systems, while unintentional sources might be everyday electronics that emit radio frequencies as a byproduct of their operation. In critical applications, such as aerospace and defense, RFI can have serious consequences, potentially leading to loss of communication or navigational errors.

The Importance of EMI/RFI Shielding
Given the potential impacts of EMI and RFI, it becomes evident why shielding is necessary. Shielding serves to protect electronic devices and systems from these types of interference, ensuring their proper function in a wide range of environments.
Shielding works by creating a barrier that blocks or attenuates electromagnetic waves, preventing them from reaching sensitive components. This is typically achieved through the use of materials that are either conductive or magnetic, or both, as these materials can reflect, absorb, or redirect the electromagnetic energy.
The Role of RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets
In the context of shielding, RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets play a vital role. These gaskets are specifically designed to provide a continuous shielding barrier at the seams and joints of electronic enclosures. Because seams and joints are often the weakest points in a shielded enclosure, they require particular attention to ensure that the shielding is effective.
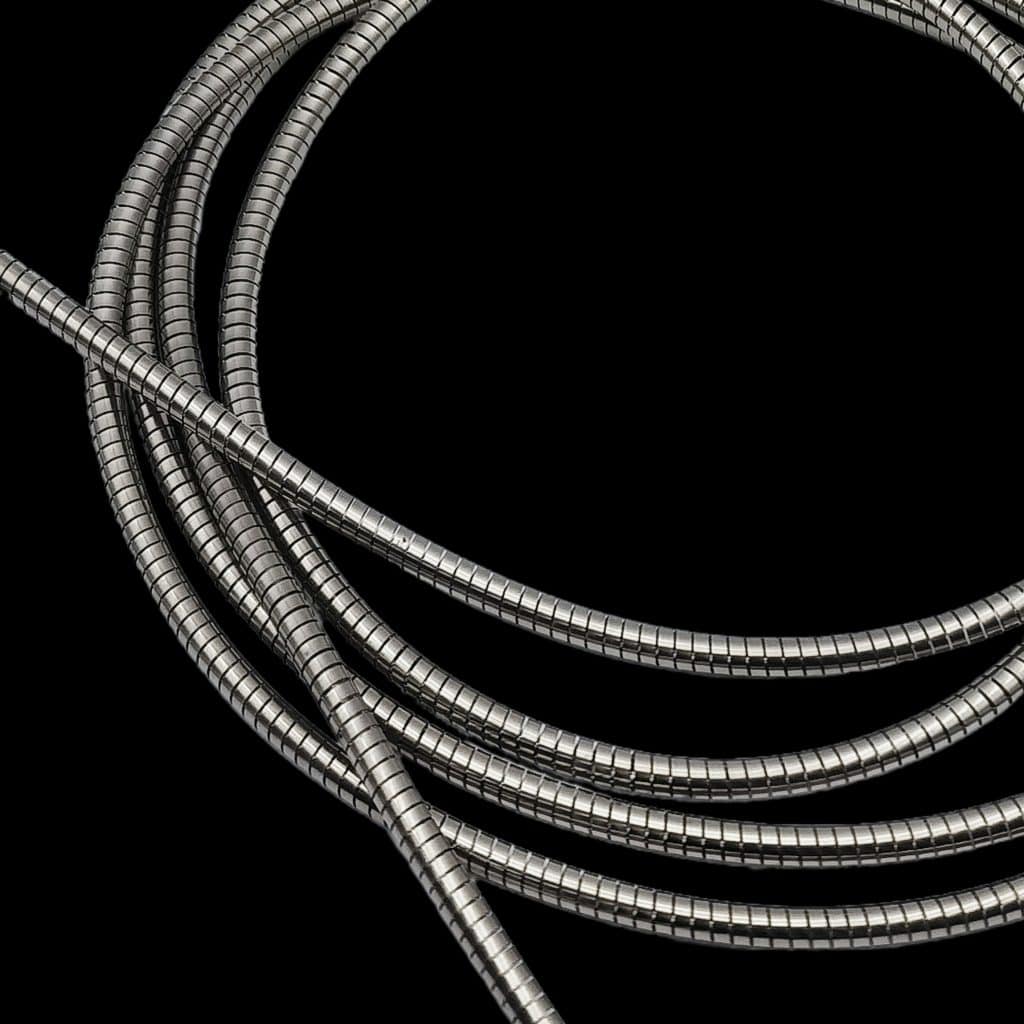
Design and Construction of RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets
The design of RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets is a key factor in their effectiveness. These gaskets are typically constructed with a spiral configuration, which provides several advantages in terms of shielding performance and flexibility.
- Spiral Configuration: The spiral pattern is integral to the performance of these gaskets. The spiral design creates a dense network of conductive paths, which is crucial for intercepting and dissipating electromagnetic waves. The density and continuity of these paths ensure that the gasket provides a reliable shield against EMI/RFI.
- Conductive Core: The core of the spiral gasket is usually made of a highly conductive material, such as a metal-filled elastomer or a conductive fabric. This core material serves as the primary pathway for electromagnetic energy, allowing the gasket to effectively absorb or reflect incoming waves.
- Outer Layer: The outer layer of the gasket is often made of a more flexible, resilient material, which allows the gasket to conform to irregular surfaces and maintain a tight seal. This outer layer is also designed to be resistant to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, UV light, and chemical exposure, ensuring that the gasket remains effective over time.
- Compression and Resilience: One of the key characteristics of spiral gaskets is their ability to compress and return to their original shape. This resilience is important because it ensures that the gasket maintains continuous contact with the mating surfaces, providing a consistent shielding effect even under conditions of mechanical stress or thermal expansion.
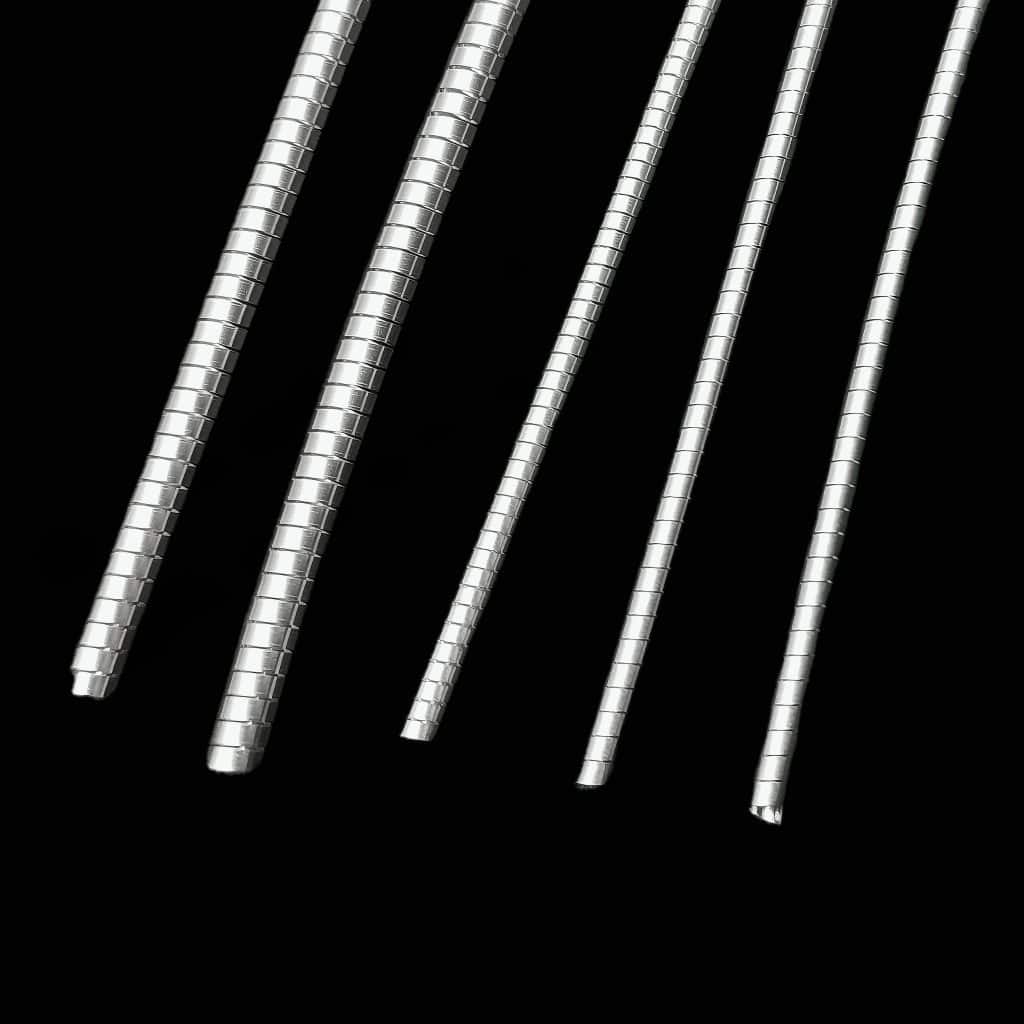
How EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets Block Electromagnetic Interference
The effectiveness of EMI shield spiral gaskets can be attributed to several factors:
- Conductive Pathways: The primary mechanism by which these gaskets block EMI is through the creation of conductive pathways. These pathways allow the gasket to either absorb or reflect the electromagnetic waves, preventing them from penetrating the enclosure. The spiral design enhances this effect by creating multiple, overlapping pathways, which increases the overall shielding effectiveness.
- Low-Impedance Pathway: Another important factor is the gasket’s ability to create a low-impedance pathway for electromagnetic energy. Impedance is a measure of how much a material resists the flow of electric current. A low-impedance pathway allows the electromagnetic energy to be redirected away from sensitive areas, effectively containing it within the shielded enclosure.
- Sealing Effectiveness: The spiral design of these gaskets also contributes to their sealing effectiveness. By filling gaps and openings completely, the gasket prevents electromagnetic waves from leaking through. This is particularly important in environments where even small amounts of EMI/RFI can cause significant problems.
- Material Selection: The materials used in EMI shield spiral gaskets are chosen for their specific properties, including electrical conductivity, durability, and environmental resistance. Common materials include nickel, iron alloys, copper, aluminum, and silver. Each of these materials offers different levels of conductivity and shielding effectiveness, allowing manufacturers to select the most appropriate material for a given application.
Applications of RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets
RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets are used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to critical infrastructure. Below are some of the key industries and applications where these gaskets play a crucial role:
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, EMI and RFI can cause significant issues, including poor signal quality, reduced battery life, and even device malfunction. As devices become more compact and feature-rich, the potential for interference increases, making effective shielding more important than ever. RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other portable devices to protect sensitive components from interference.

Telecommunications
The telecommunications industry relies heavily on RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets to ensure the integrity of signals in wireless communication systems. These gaskets are used in base stations, antennas, and other communication infrastructure to prevent RFI from degrading signal quality. In this industry, even minor interference can lead to significant issues, such as dropped calls, slow data speeds, and network outages.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, the consequences of EMI and RFI can be life-threatening. Medical devices, such as pacemakers, MRI machines, and diagnostic equipment, must operate without interference to ensure accurate readings and proper functioning. RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets are used to protect these devices from external electromagnetic fields, ensuring patient safety and reliable operation.

Aerospace and Defense
Aerospace and defense applications often operate in environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference, such as near radar installations or in combat zones. In these scenarios, the failure of electronic systems due to EMI or RFI can have catastrophic consequences. RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets are used extensively in military equipment, aircraft, and spacecraft to protect sensitive electronics from interference and ensure mission success.

Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is increasingly reliant on electronics for everything from engine control units to infotainment systems. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the potential for EMI and RFI interference increases. RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets are used in automotive electronics to prevent interference from affecting critical systems, such as braking, steering, and communication.

Conclusion
In conclusion, RF/EMI shield spiral gaskets work by utilizing their conductive properties and unique spiral design to create a continuous, low-impedance pathway that blocks or redirects electromagnetic interference away from sensitive electronic components. Through careful material selection and customization, these gaskets provide a critical layer of protection for electronic devices in environments prone to electromagnetic interference.