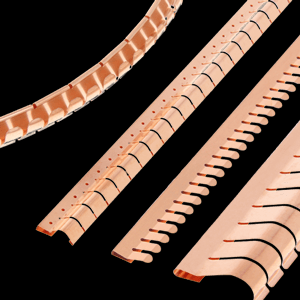
Right-angle shielding fingerstrips/angled fingerstocks
Right-angle shielding fingerstrips, also known as angled fingerstrips, are specialized components designed to manage electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) in electronic systems. These fingerstrips are particularly useful in configurations where electronic components intersect at a 90-degree angle. Their primary role is to ensure effective shielding, maintaining electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and protecting sensitive electronic equipment from interference.
Introduction
Right-angle shielding fingerstrips, also known as angled fingerstrips, are specialized components designed to manage electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) in electronic systems. These fingerstrips are particularly useful in configurations where electronic components intersect at a 90-degree angle. Their primary role is to ensure effective shielding, maintaining electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and protecting sensitive electronic equipment from interference.
Table of Contents
Design and Functionality
Purpose and Importance
The main purpose of right-angle shielding fingerstrips is to provide reliable EMI/RFI shielding in electronic setups with perpendicular component arrangements. When electronic devices have components aligned at right angles, traditional shielding solutions might not be effective due to gaps or incomplete coverage. Right-angle fingerstrips address this issue by ensuring continuous shielding across these angular junctions, which is crucial for maintaining the performance and reliability of electronic systems.
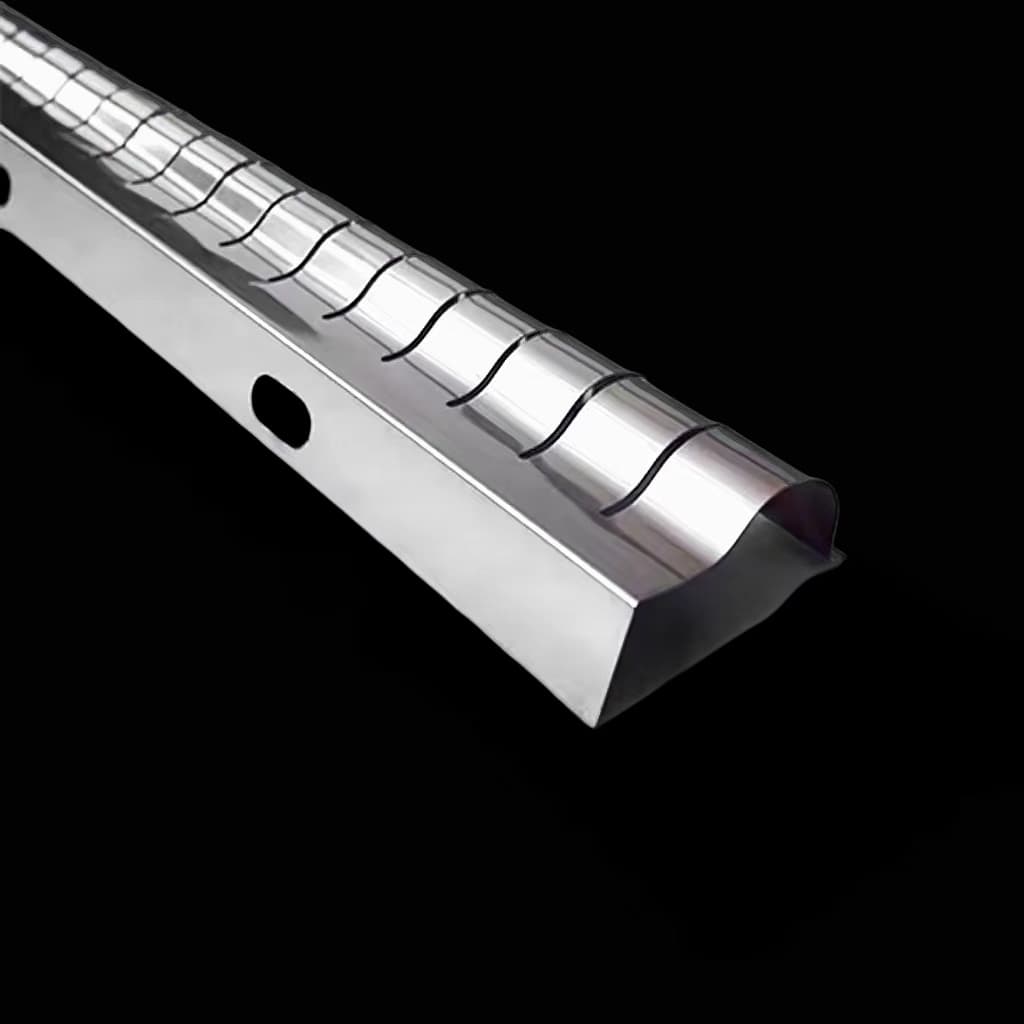

Applications
Right-angle shielding fingerstrips are used in a wide range of applications:
- Computer Hardware: To shield critical internal components from electromagnetic emissions that could cause operational issues or data corruption.
- Telecommunications Equipment: To prevent signal interference and ensure the integrity of communication systems.
- Automotive Electronics: To protect sensitive electronic control systems from EMI that could impact vehicle performance.
- Shielded Enclosures: In shielded chassis and nacelles, these fingerstrips maintain the effectiveness of the shielding enclosure.
- Specialized Environments: In laboratories, darkrooms, and areas where precise control over electromagnetic fields is required, right-angle shielding fingerstrips help create controlled environments free from external interference.
Specifications and Materials
Materials
The choice of material for right-angle shielding fingerstrips significantly affects their performance and durability. Common materials include:
- Beryllium-Copper: This material is favored for its high electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and excellent fatigue strength. Beryllium-copper alloys ensure effective EMI shielding and are durable under mechanical stress.
- Stainless Steel: Known for its strength and resistance to environmental factors, stainless steel is used in applications requiring robustness, although it may offer slightly lower conductivity compared to beryllium-copper.
- Phosphor Bronze: This alloy combines good conductivity with mechanical strength and is used in specific applications where these properties are crucial.
- Tin-Plated Variants: These provide enhanced corrosion resistance and a more robust shield against environmental degradation, extending the lifespan of the shielding component.
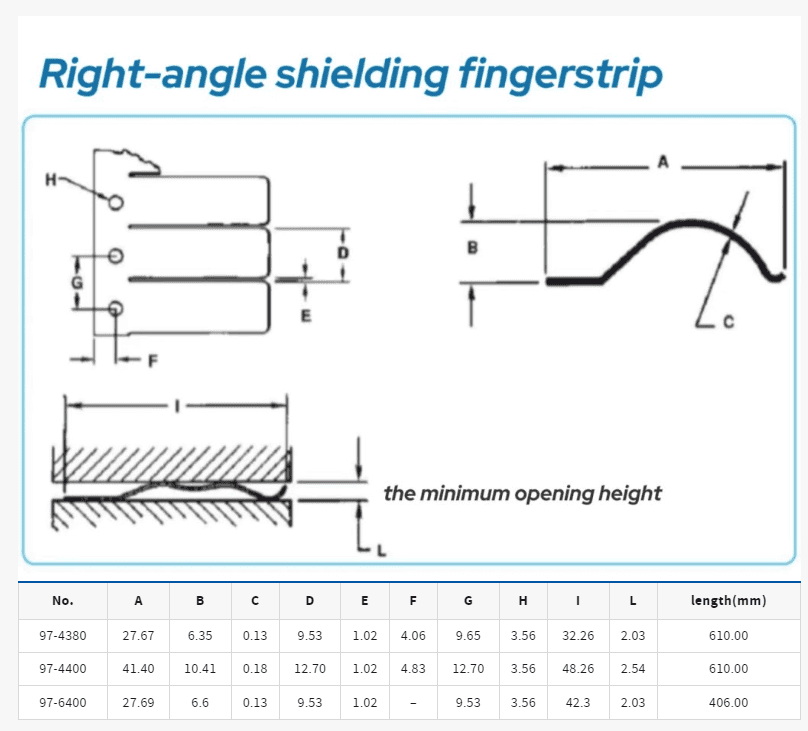
Dimensions
The dimensions of right-angle shielding fingerstrips vary depending on the specific application and manufacturer. Key dimensions include:
- Length: The length of the fingerstrip should be sufficient to cover the area where the components meet.
- Width and Thickness: These dimensions determine the fingerstrip’s ability to compress and maintain effective contact with the surfaces being shielded.
- Angles and Cuts: Specific angles and cuts are tailored to fit the precise geometric requirements of the electronic setup.
Customization options are often available to meet the unique needs of different applications, ensuring that the shielding effectiveness is not compromised.
Installation Considerations
Alignment and Compression
Proper installation is critical to achieving optimal performance from right-angle shielding fingerstrips. Factors to consider include:
- Alignment: The fingerstrips must be accurately aligned with the surfaces they are meant to shield. Misalignment can lead to gaps and reduced shielding effectiveness.
- Compression: The fingerstrips must be compressed correctly to ensure full contact with the surfaces, which is necessary for effective EMI/RFI shielding. Excessive or insufficient compression can affect the overall performance.
Tools and Techniques
Specialized tools or techniques may be required for precise installation, especially in confined or complex configurations. Proper training or experience is often necessary to ensure that the installation does not inadvertently damage the components or the fingerstrips.
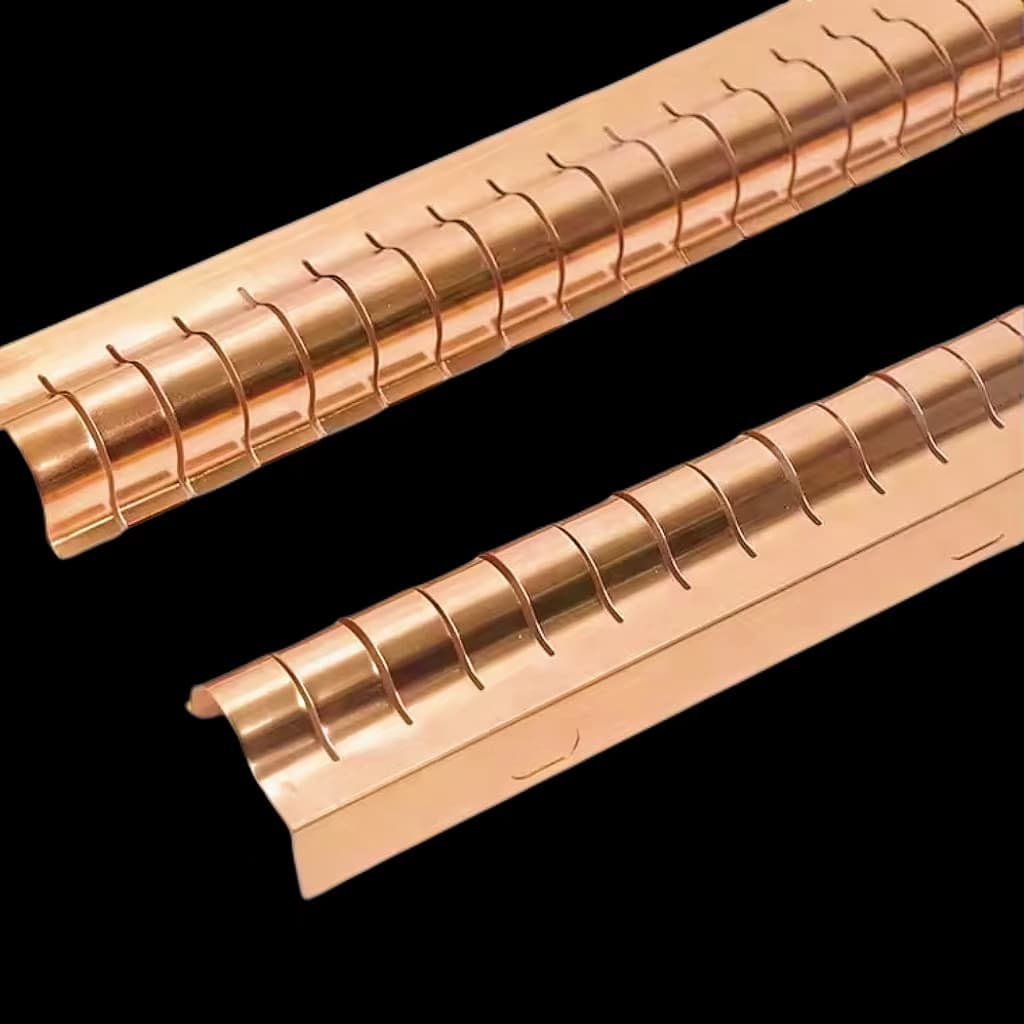

Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of right-angle shielding fingerstrips involves several critical steps:
- Design and Dimensioning: The initial phase includes creating detailed designs and dimensions based on the application requirements. CAD models and simulations may be used to refine the design.
- Fabrication: This involves cutting, stamping, or photoetching the material into the required shape. Complex designs may use photoetching to achieve intricate patterns and precise dimensions.
- Material Preparation: The selected materials, such as beryllium-copper or stainless steel, are prepared for processing. This includes any necessary treatments to ensure optimal performance.
- Surface Treatment: Surface treatments like tin plating are applied to improve corrosion resistance and enhance the durability of the fingerstrips.
- Assembly and Testing: The fingerstrips are assembled and subjected to rigorous testing to verify their shielding effectiveness and mechanical properties. This step ensures that the final product meets the required standards and specifications.
- Packaging: Proper packaging is essential to protect the fingerstrips from damage during transport and storage. Packaging must also ensure that the components are handled carefully to avoid any physical damage that could impact their performance.
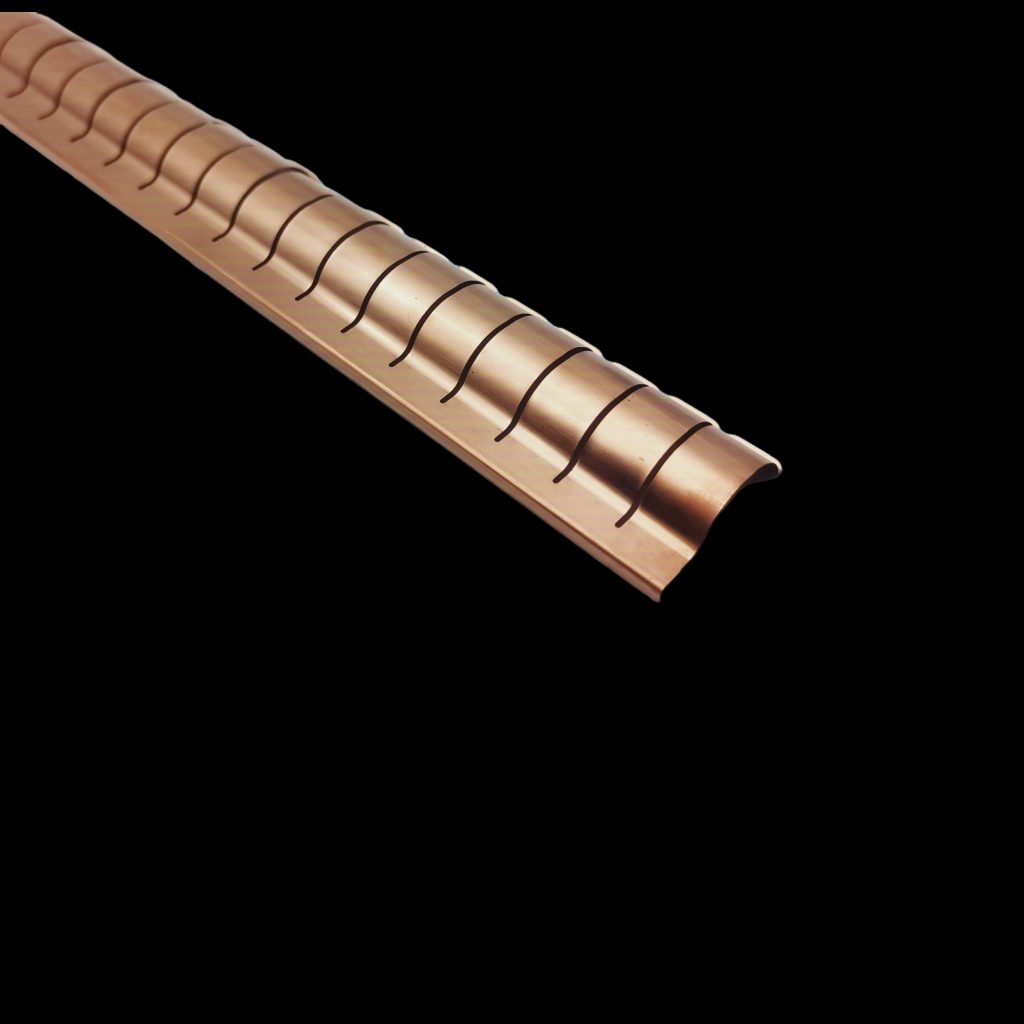

Benefits
Durability and Compression Range
Right-angle shielding fingerstrips are designed to be durable and maintain their effectiveness over a wide compression range. This ensures that they can withstand the pressures and stresses of installation and operation without compromising their shielding performance.
Grounding Performance
These fingerstrips provide excellent conductive grounding, which is essential for effective EMI/RFI shielding. Proper grounding helps in preventing electromagnetic interference from affecting electronic systems.
Mechanical Strength
The materials used in right-angle shielding fingerstrips offer excellent mechanical strength, allowing them to endure the physical stresses associated with installation and operation without deformation or failure.
Temperature Stability
Right-angle shielding fingerstrips perform reliably across a wide range of temperatures. This makes them suitable for use in various environments, from extreme cold to high heat, without loss of shielding effectiveness.
Customization
Many manufacturers, such as Handa Shielding, offer custom solutions tailored to specific application needs. Custom options may include specialized dimensions, materials, and surface treatments, ensuring that the fingerstrips meet the exact requirements of the application.
Conclusion
Right-angle shielding fingerstrips are vital components for effective EMI/RFI management in electronic systems, particularly where components intersect at right angles. Their design, material selection, and manufacturing processes are carefully engineered to ensure optimal performance, durability, and reliability. By providing comprehensive shielding solutions and addressing complex geometric challenges, these fingerstrips play a crucial role in maintaining the performance and integrity of electronic devices and systems across various applications.
You May Also Like
-
 RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets: Essential Components for Electromagnetic Compatibility
RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets: Essential Components for Electromagnetic CompatibilityEMI/EMC Shielding | RFI Shielding | EMI Gaskets
RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gasket
In today's interconnected world of electronics and telecommunications, maintaining electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability of electronic devices. RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets play a pivotal role in achieving this goal by effectively mitigating electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can disrupt signal integrity and functionality. What are RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets?Key Features and BenefitsApplications Across Industries What are RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets? RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets are specialized components designed to provide robust shielding against electromagnetic radiation. They are typically made from conductive materials such as metal alloys or conductive elastomers, crafted into a spiral shape that allows them to conform closely to mating surfaces. This design ensures consistent contact and compression, optimizing the gasket's ability to block EMI effectively. Key Features and Benefits EMI Shielding Effectiveness: The primary function of RF/EMI Shield Spiral Gaskets is to attenuate electromagnetic waves, preventing external interference from disrupting sensitive electronic signals. This capability is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and preventing data corruption in telecommunications, aerospace, medical devices, and industrial automation. Versatility in Applications: These gaskets are available in various sizes, shapes, and materials to suit different application requirements. They are commonly used in:Telecommunications: Ensuring clear and reliable communication by......
-
 Handa Shielding – Clip-on mounting fingerstrip
Handa Shielding – Clip-on mounting fingerstripFingerstrips
Clip-on mounting shielding fingerstrip
Clip-on mounting fingerstrip gaskets are essential components in the realm of electromagnetic shielding, playing a critical role in ensuring the effective performance of electronic devices and systems. These gaskets, produced by leading manufacturers like Handa Shielding, are designed to provide reliable electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and grounding. This article explores the construction, types, features, and applications of clip-on mounting fingerstrip gaskets, with a focus on Handa Shielding’s offerings. IntroductionConstruction and MaterialsTypes of Clip-On Mounting Fingerstrip GasketsMain Features of Clip-On Mounting Fingerstrip GasketsTypical ApplicationsConclusion Introduction In the world of electronics, electromagnetic shielding is crucial for preventing interference and ensuring the optimal functionality of devices. Fingerstrip gaskets are a key element in this shielding process, providing a conductive pathway that helps maintain signal integrity and reduce EMI. Handa Shielding, a prominent supplier in the shielding industry, offers a range of solutions including both stick-on and clip-on mounting fingerstrip gaskets. While stick-on gaskets are useful for general purposes and fit into confined spaces, clip-on mounting fingerstrip gaskets are engineered for more specialized requirements, particularly in challenging environments. Clip-on mounting fingerstrip gaskets are especially valuable in high-temperature environments and other demanding conditions where traditional stick-on solutions may be inadequate. This article provides an in-depth......
-
 Electrical Conducting Canted Coil Springs
Electrical Conducting Canted Coil SpringsHanda Canted Coil Springs
Electrical conducting springs
Electrical Conducting Springs In the fields of electrical and mechanical engineering, electrical conducting canted coil springs have emerged as pivotal components due to their unique blend of electrical conductivity and mechanical robustness. This article provides an in-depth examination of canted coil springs, focusing on their design, performance, applications, and customization. By understanding these aspects, engineers can better utilize these springs to enhance the performance and reliability of their systems. The Essence of Electrical Conducting Canted Coil SpringsVersatile ApplicationsPerformance FactorsMaterial ChoicesCustomization and AvailabilityOrientation and DesignConclusion The Essence of Electrical Conducting Canted Coil Springs Electrical conducting canted coil springs are distinguished by their angled coil configuration, which sets them apart from traditional springs. This design feature enables a compact footprint, allowing for the management of more power in less space while maintaining cooler operating temperatures. The coil's angled arrangement not only optimizes space but also improves heat dissipation. This is particularly advantageous in applications where heat management is crucial, as it minimizes heat rise and ensures a consistent, reliable electrical connection even under shock and vibration. The design of electrical conducting canted coil springs involves winding a wire into a helical shape and then angling it slightly. This results in a spring......
-
 Aluminium Foil in Electromagnetic Shielding
Aluminium Foil in Electromagnetic ShieldingEMI tapes, EMC foils, conductive textiles & half conductive non-woven
Conductive aluminium tape
Aluminium foil, a widely recognized material in both household and industrial applications, is particularly valued for its role in electromagnetic shielding. This article delves into the properties, applications, and considerations surrounding the use of aluminium foil for electromagnetic shielding. Its effectiveness and versatility make it a staple in numerous settings, from laboratories to consumer electronics, but it also presents certain challenges that must be addressed for optimal performance. Properties of Aluminium FoilApplicationsConsiderationsConclusion Properties of Aluminium Foil Aluminium foil is renowned for its lightweight and conductive characteristics, which play a crucial role in electromagnetic shielding. Its ability to reflect and absorb electromagnetic waves is central to its effectiveness in minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI). Specifically, aluminium foil is capable of reflecting over 88% of incident electromagnetic waves in the X-band frequency range, a testament to its efficiency in shielding applications. This reflective property is beneficial for protecting sensitive electronic components from external interference, which is vital in maintaining the integrity and performance of various devices. Applications 1. EMC Shielding In electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) laboratories, the foil is commonly employed to diagnose and address sources of EMI. Its role is primarily temporary, serving as a quick solution to isolate and protect circuits from......
-
 Electrical Contact Finger Springs
Electrical Contact Finger SpringsEMI/EMC Shielding | RFI Shielding | EMI Gaskets
Fingerstrips
Introduction to Contact Finger Springs Contact finger springs are crucial components in the field of electronics and electrical engineering. They play a pivotal role in ensuring reliable electrical connections in a wide array of devices and systems. Understanding these components involves delving into their design, function, materials, and applications. This comprehensive exploration will cover all these aspects in detail. Introduction to Contact Finger SpringsDefinition and PurposeDesign and FunctionalityMaterials and ManufacturingApplicationsBenefits and LimitationsFuture Trends and DevelopmentsConclusion Definition and Purpose Contact finger springs, also known as contact springs or finger contacts, are spring-loaded elements designed to provide a stable and consistent electrical connection between two conductive surfaces. Their primary purpose is to maintain a secure and reliable electrical connection by applying a constant force between the contacts, which helps to minimize issues like intermittent connections, wear, and poor conductivity. Design and Functionality 1. Design Elements Shape and Structure: Contact finger springs are typically designed with a specific geometric shape that allows them to compress and return to their original form. Common designs include flat, curved, or cylindrical shapes. The design often resembles a comb or series of fingers, which is why they are sometimes referred to as "finger" springs. Material Composition: The......